Image from http://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S0009898102001821-gr1.jpg, Last accessed 15/01/2013
0 Comments
Treatment
oral carnitine supplementation -> slow increase of plasma carnitine levels In acute situations, if the patient presents with hypoketotic hypoglycemic encephalopathy stabilize with 10% dextrose in water intravenous (IV) Patients with primary carnitine deficiency, requires no special diet as long as they are taking carnitine supplementation Patients with fatty acid oxidation disorders require a high-carbohydrate fat-restricted diet Strenuous activity should be avoided, frequent snacks and good hydration should be procured along with physical activity. Complications Fat accumulates in the liver, skeletal muscle and heart, impair organ/tissue function Fat cannot be utilized, glucose is consumed without regeneration, drop in glucose levels Impairing of brain function and loss of consciousness. Mutations in the OCTN2 carnitine transporter in primary carnitine deficiency.
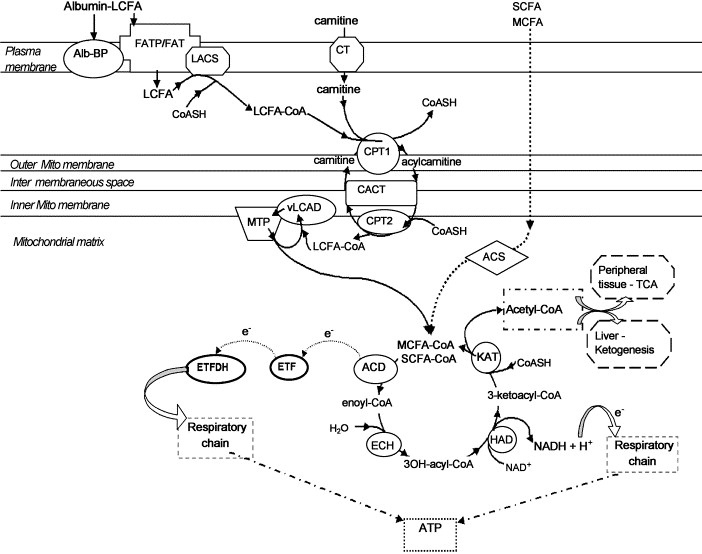
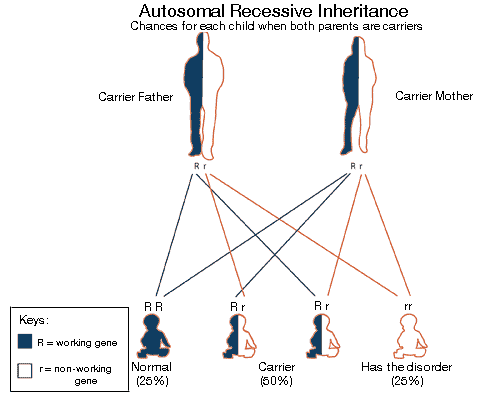
SLC22A5 (gene) located Chromosome 5 (human) causes defective OCTN2 It is an autosomal recessive disease characterized by low serum and intracellular carnitine concentration. Intracellular carnitine deficiency impairs the entry of long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondrial matrix. Thus body fat cannot be used. The lack of the transporter causes urinary carnitine wasting and low serum carnitine levels. leading to reduced intracellular carnitine accumulation. Regulation of the intramitochondrial CoA is affected, then acyl-CoA esters accumalate in the mitochondria.Which affects the pathways of intermediary metabolism that require CoA. This causes disorder of fatty acid oxidation. Excessive accumulation of lipids occurs in the muscles, heart and liver.  Individuals who are diagnosed with mitochondrial disease have to monitor their nutrition with great care to have sufficient intake of especially proteins and carbohydrates. Calorie intake must be carefully measured.
Hydration also plays a huge part in the health of a cell so mito patients must also watch this aspect of it. Protein intake is vital because carbohydrate spikes will cause mitochondria to break down glucose into ATP for cellular function, this effect is harmful and not produced in intake of protein. Generally, a diet of protein and a complex carbohydrate like rice at each meal and avoidance of fasting to maintain a healthy hydration levels will allow for more normal functioning of the body in mito patients. Link- http://www.mitoaction.org/blog/nutrition-mitochondrial-disease-patients Carnitine facilitates the body to utilize fat(lipid oxidation) for energy.
It is used to transport long chain fatty acids to mitochodria. It is also known as a vitamine and amino acid like substance. it is produced in the liver and kidneys and stores it in the skeletal muscles, heart, brain, and sperm. Normally the body is able to produce sufficient amounts of carnitine. Source: http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/carnitine-l-000291.htm#ixzz2HwJRggZz Follow us: @UMMC on Twitter | MedCenter on Facebook Mitochondrial diseases arise from spontaneous mutations in mtDNA or nDNA which gives rise to errors in protein expression; which may ultimately lead to failure.
Thus there can be many different types of mitochondrial diseases which each produce different types of symptoms. Defining the cause of the disease is significantly harder due to the range of symptoms which make it hard to categorize them into a single spectra of a disease. These are classified under Genocopies: which are diseases with the same mutation but produce different phenotypes. And Phenocopies: where different mutations in mtDNA and nDNA lead to the same type of disease. Failure in mitochondrial activity in cells will lead to a loss of energy produced by cells which may lead to the cells starting to deteriorate and subsequent organ failure. Most notably the renal, endocrine, neuromuscular failure. Link: http://www.umdf.org/site/c.8qKOJ0MvF7LUG/b.7934627/k.3711/What_is_Mitochondrial_Disease.htm As seen here, the CPT-1 transporter is a crucial step in the mitochondrial space which transports carnitine into the mitochondrial matrix and is crucial for fatty acid metabolism
Image last accessed 16/01/2013. Image from :http://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1050173802001846-gr1.jpg This area is used to post all article links relevant to our project, with references in the next page. Both scientific sources and other sources will be noted down here. Each post will have a short description of the article that is related and the informtat
 Diagnosis of CPT-1 deficiency is done by blood tests.
-Hyperketotic Hypoglycemia (blood glucose concentration < 40mg/L) -Elevated ammonia levels (100-500 umol/L where normal < 70umol/L) -Elevated total carnitine levels ( 70-170 umol/DL) where normal serum (25-69umol /DL) This is mostly done in newborn screening programs, but a competent healthcare provider can also do blood test screenings. Diagnosis of Obesity is usually done by Body Mass Index Underweight: BMI <18.5 Normal Weight: BMI 18.5 - 24.9 Overweight: BMI 25-29.9 Obesity: BMI >30 More information can be available on NCBI website - Link : http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1527/ Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1A Deficiency |

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed