 Study done by NCBI on olive oil polyphenols hydroxytyrosol were done by a group of scientists in 2011.
Human keratinocytes were grown in appropriate medium and cultured in various concentration os hydroxytyrosol and cell cycles were analysed by flow cytometry to count the number of cells in each phrase.
The growth and health of these cells were tested by various methods including yH2AX immunofluorescence, clonogenic survival.
Generally results were shown that cells cultured in presence of hydroxytyrosol were more radiation resistant. They showed characteristics like increased expression of genes of DNA replication, repair gene Artemis,( which plays a major role as a nuclease and DNA repair pathway), changes in inflammatory associated genes and upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines which are beneficial to mitochondrial signalling.
Other important findings relevant to our project is the fact that there is increased breakdown of heme, which is available in blood, due to a 15.5 times upregulation of enzyme heme oxygenase (HO-1). which is a pro-oxidant and indicative of liver health. Biliverdin, which breaks down to bilirubin is usually tested in liver health tests in urine samples where positive samples indicate some sort of liver disease like NAFLD.
Thus the upregulation of enzyme HO-1 produces a reduction in oxidative stress.
Glutaredoxin has also been proven to have increased levels, where its functions are to reduce oxidative stress by protecting thiol bonds.
Glutathione peroxidase 3 is also another antioxidant enzyme which has seen an increase, involved in catalysing the reduction of NAD, quiones, which are all available in the respiratory pathways.
Thus overall indicating that olive oil has a beneficial effect as a dietary supplement for obesity patients and patients with mitochondrial and fatty acid disorders.
Last Accessed 14/01/2013. Haloom Rafehi,1,2 Andrea J. Smith,3 Aneta Balcerczyk,4 Mark Ziemann,4 Jenny Ooi,4 Shanon J. Loveridge,1,4 Emma K. Baker,4,7 Assam El-Osta,2,4,5,6 and Tom C. Karagiannis1,2. (2011). Investigation into the biological properties of the olive polyphenol, hydroxytyrosol: mechanistic insights by genome-wide mrna-seq analysis. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3316757/
Mitochondria Image: http://1.bp.blogspot.com/-GWDahOB2IFk/T5jgR593gBI/AAAAAAAABQg/O4GJ00nPsjk/s1600/Mitochondria.jpg
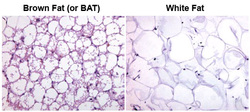 As reported from NCBI with a study on types of fat intake and BMI relation to obesity, There are 3 different types of body fat that are stored in the body. Brown fat- which can burn calories and maintains body warmth. It has even been proven to burn white fat. White fat - which produces a hormone called adiponectin which stimulates liver and muscle cells to be more sensitive to insulin effects, which decreases chances of diseases like diabetes and obesity. Visceral fat - Which occurs in the belly and other parts which is harmful to our body and play a large role in insulin resistance which leads to diabetes and other liver disorders. NCBI article Link: Last accessed 14/1/2013 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10979153Non-Scientific Link: http://www.webmd.com/diet/features/the-truth-about-fat
NAFLD
Increased visceral (around organs) adiposity and insulin resistance (IR).Insulin resistance in the liver is associated with more hepatic glucose output due to insulin-suppressing effects on gluconeogenesis being impaired. Worsening hyperglycemia, resulting to type 2 diabetes. Peripheral IR (adipose tissue, skeletal muscle) causes increased free fatty acids (FFA) which move to the liver increased hepatic fatty acid synthesis and FFAs results in increased triglyceride accumulation in the liver. FFA re-esterification process causes long-chain acyl-CoAs and diacylglycerol (DAG) to accumulate. Excess FFAs prevents kinase interaction with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activation. The FFA-induced down-regulation of insulin signaling pathways results in several kinases involved in stress response being activated. Which will lead to the activation of numerous pro-inflammatory cytokine genes (IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α) which are involved in promotion of IR. this chain reaction will reduce insulin sensitivity and increase liver injury. Hepatic and peripheral IR along with altered lipogenesis will contribute in NAFLD progression. Hepatic IR will cause an increase expression of element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c). Increase of SREBP-1c will have an effect down stream which will cause inhibition of carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1 (CPT-1). CPT-1 inhibition will result in decreased oxidation of fatty acids increasing the amount of FFAs in the liver. When there is too much fatty acids stored in the body, it will ultimately lead to obesity.
Primary carnitine deficiency
Due to a mutation in the DNA, there is reduced amount of carnitine in the tissue, due to the carnitine being discharged in the urine. Similar to NAFLD, this causes the body to loss the ability to utilize fat and causing a build up of fat in the body. When there is excess fat stored in the body, it will lead to obesity.
The thyroid gland plays a very important role in mitochondrial activity and Iodine levels have a direct correlation between hyperthyroidism which may lead to weight gain due to lack of mitochondrial production.
- Intake of sea vegetables is a good source of Iodine to help regulate this problem.
Decreased levels of ATP is also affected by oxidative damage to mitochondrion which causes damage to the respiratory chain and thus effective glucose / fatty acid metabolism.
- Intake of antioxidants like green tea and coffeeberry forte can reduce oxidative damage.
- Intake of alpha lipiotic acid also improves mitochondrial health, this comes from olive oil.
Olive Oil abstracted from Olea Europaea: Contains chemical hydroxytyrosol which is a strong antioxidant and has anti-cancer properties. More specifically, it had P-glycoprotein modulating activity which overall produces a reduction in oxidative stress on the mitochondrion. It is also proven to alter lipid profiles where there is better cholesterol levels which prevent atherocelerosis. Likewise, it reduces hypertension and improves diabetes (insulin resistance).
Proven to improve production of Coenzyme Q which is in the respiratory pathway in mitochondrion is a sign of protection as antioxidant.
.
Links :
http://www.getprograde.com/optimizing-mitochondria-for-healthy-weight-loss.html
From NCBI article: Investigation into the biological properties of the olive polyphenol, hydroxytyrsol: mechanistic insights by genome-wide mRNA seq analysis/ Published online 2011 September 28 by Haloom Rafehi et al / Last Accessed : 12.01.2013, 10pm/http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3316757/
1- "Nutrient excess leads to mitochondrial dysfunction, which in turn leads to obesity related pathologies."
2- Insulin resistance is a key indicator of type 2 diabetes. Which is linked to obesity whereby there is reduction in efficiency of glucose and fatty acid metabolism,and decreased glycogen synthesis. Recent studies are focused on the link between mitochodrial dysfunction and insulin resistance
1. Abstract from NCBI/Last Accessed 12/01/2013, 9.29pm/ Website : http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20585248
2. Information from: Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity by Kurt Højlund, MD, PhD et al./ Last Accessed 12/01/2013, 9.29pm/ Website : http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0889852908000340
Increase Risk
-overweight
-have type 2 diabeties (increased liver uptake of fat)-Systemic carnitine deficiency
-have high blood pressure-high cholesterol
-experienced extreme weight loss
Treatment
-Liver Transplantation, when NAFLD progresses to liver failure
-No standard treatment exists.
-Weight loss, when have elevated blood lipids/obese
-Control blood sugar, diabetic
Prevention
-Healthy diet
-Heathy weight
Mitochondrial abnormalities are closely related to NAFLD
NAFLD may be a mitochondrial disease
Abnormalities include:
-ultra structural lesions
-depletion of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
-decreased activity of respiratory chain complexes
-impaired mitochondrial β-oxidation
During NAFLD, the , mitochondria is big and swelled, scarce in number and the matrix has para crystalline inclusions and hypo density.
Patients treated with a drug(4,4'-diethylaminoethoxyhexestrol) that inhibits
mitochondrial respiratory chain (MRC) activity & mitochondrial β-oxidation, show
the same mitochondrial lesions.
NAFLD is often found in patients with insulin resistance, obesity and type 2
diabetes, decresed O2 consumption and ATP production, decresed total mtDNA and
mtDNA transcription factor A and reduced content of respiratory proteins in the
fat, muscle and liver.
mtDNA depletion in hepatocytes (liver tissue) impairs mitochondrial function
causing hepatic steatosis and other liver injury.
A single symptom can be caused by many things whereas more than one syndrome can have similar causes. Eg. COX deficiency or Complex I/ Complex II deficiency come under general diagnosis of respiratory chain deficiencies.
Generally, the lack of energy synthesized by mitochondria leads to cell damage which could lead to a wide term of disorders under mitochondrial encephalomyalpathy; which affect specifically the respiratory chain (nothing to do with breathing).
Nuclear DNA mutations: Are less disastrous and easier to predict as most diseases like Leigh Syndrome ( defects caused in Complexes I and IV) are autosomal recessive which requires two copies of the gene for a phenotype to be seen. Thus less likely to be in effect.
Eg. Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders (FAODs are autosomal reccessive)
Mitochondrial DNA mutations: Are more disastrous as they do not follow traditional Mendelian pattern of Inheritance where one set of genes come from the father and mother each. 100% of mitochondrial genes come from the maternal side only thus mutations are higher in ratio. Also, when a mutation occurs in mtDNA, heteroplasmy (where only some of the genes contain the mutation and not all) occurs, which gives us a very large range of diseases of varying severity that could arise in an individual. This is made even more unpredictable such that while only the mother passes on the mtDNA to the infant, it is not known how much of the maternal mtDNA is passed on during each reproduction.
Eg.
MERFF(Myoclonus epilepsy with ragged red fibers)
NARP (Neuropathy, ataxia and retinitis pigmentosa)
MELAS (Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic acidosis and strokelike episodes)
Spontaneous DNA mutations: Where both the mother and father do not have the disease and are usually caused by deletions.
Eg.
KSS(Kearns Sayre Syndrome which may cause eye problems, mental retardation)
PEO(Progressive External Opthalmolagia which affects eyes)
Pearson's Disease( Severe Anaemia and Pancreas malfunction)
Combination of nDNA + mtDNA mutations: Which are inherited by Mendalian Genetics patterens but also has mtDNA deletions.
Eg.
MNGIE(where a gene coding for thymidine phosphorylase is defunct in producing mitochondrial proteins)
Link- Mitochondrial Research Society http://www.mitoresearch.org/mitodiseases.html
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Healthy liver has little or no fat, in NAFLD 5% of hepatocytes show lipid droplets exciding 5-10% of liver weight
most people with NAFLD may show no syntom and no complications.
Important key factors
-Obesity
-hyperglycemia
-type 2 diabetes
-hypertriglyceridemia
-Genetic factors
Syntoms
-Fatigue
-exercise intolerance
-vague abdominal pain in the right upper quadrant
Diagnosis of NAFLD
Blood tests
Liver ultrasound, an imaging procedure, where shape & consistency of liver is shown
liver biopsy is used for some cases which there is a need for definite diagnosis. And defining stage ans severity of inflamation
Stages of NAFLD
Stage 1: simple fatty liver
Excess fat builds up in the liver cells. Usually no symptoms shown
Stage 2: non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
Only few people develop to stage 2. at this stage it is more aggressive (liver inflamed)
May have a dull pain in top right of abdomen
Stage 3: fibrosis
Persistent inflammation leading to generation of fibrous tissue replacing healthy tissue
liver has enough tissue to operate normally.
Stage 4: cirrhosis
Most server stage. Liver shrinks and becomes clumpy. occur after the age of 50-60 due to prolonged inflammation. Often also leads to type 2 diabetes. Damage is permanent.
From an scientific article dated in 2009 - Mitochondrial diseases are rare thus financial support for research is limited. Likewise, the treatment of these diseases are usually dependent on a mixture of vitamins, a change of diet, and there is no universal treatment method as most are tailored to the individual. The disease is hard to diagnose due to changing diagnostic criteria and " overall lack of genotype-phenotype correlations".
Collectively, these treatments revolve around vitamin based therapies and cofactor based therapies like acyl Coenzyme A in mitochondria. Others focus on providing alternative energy source or bypassing biochemical blocks.
Current goals (2009) for these therapies are to increase ATP production and minimize free radical production which will improve overall mitochondrial health.
Ketogenic diet is recommended for mitochondrial disease patients as they have secondary fatty acid oxidation disorders. And is mainly used in treatment of pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiencyl
Some standard drugs that treat mitochondrial diseases are given in Table 2. Mitochondrial Medications and Supplements.
Mainly,
Coenzyme Q-10 ubiquinone in the form of the more absorbent ubiquinol (reduced CoQ) is found to be more absorbent and effective in treating the disease when used as a form of treatment. It is present in the electron transport chain where it transports electrons from Complex I and II from fatty acid beta oxidation to produce ATP. Thus using this as a supplement to the damaged or malfunctioning mitochondria to produce energy is a form of treatment.
Ribofavin- Essentially vitamin B2, is a precursor to riboflavin which is a key component of complex I and II in the electron transport chain and subsequent fatty acid oxidization in Kreb's cycle.
Also given are : Table 1. Drugs with reported mitochondrial toxicity
: Table 2. Mitochondrial Medications and Supplements
Link-http://www.fodsupport.org/documents/Modern-Approach-to-Treatment-of-Mito.pdf
|


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed